The Importance of Regular Health Screenings for Seniors
As we age, our health needs change significantly, necessitating more proactive and comprehensive medical care. One of the most critical components of maintaining optimal health in our senior years is regular health screenings. These screenings are designed to detect potential health issues early, when they are most treatable. This article delves into the importance of these screenings, the various types available, and how often they should be conducted to ensure seniors lead a healthy and fulfilling life.
Understanding Health Screenings
Health screenings are medical tests or procedures performed on individuals to identify early signs of diseases or conditions before symptoms appear. For seniors, these screenings can detect chronic diseases, cancer, cardiovascular issues, and other age-related health problems. Early detection often means more effective treatment and better health outcomes, which is why regular screenings are so vital.
Why Are Health Screenings Important for Seniors?
Early Detection of Diseases
The primary benefit of regular health screenings is the early detection of diseases. Many health conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, and certain cancers, may not exhibit symptoms until they have progressed significantly. Early detection through screenings allows for earlier intervention, which can prevent the disease from worsening and improve the chances of successful treatment.
Monitoring Chronic Conditions
For seniors already living with chronic conditions, regular health screenings are essential for monitoring their health status. These screenings can help healthcare providers adjust treatment plans, ensuring the conditions are managed effectively. This proactive approach can prevent complications and enhance the quality of life for seniors.
Preventive Healthcare
Health screenings are a cornerstone of preventive healthcare. By identifying risk factors and potential health issues early, seniors can take preventive measures to avoid developing serious health conditions. This can include lifestyle changes, medications, or other interventions that can significantly improve long-term health outcomes.
Common Health Screenings for Seniors
Blood Pressure Checks
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common condition among seniors and a significant risk factor for heart disease and stroke. Regular blood pressure checks can help detect hypertension early, allowing for timely management and treatment.
Cholesterol Levels
High cholesterol levels can lead to atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Screening for cholesterol involves a simple blood test that measures total cholesterol, LDL (bad) cholesterol, HDL (good) cholesterol, and triglycerides. Managing cholesterol levels through diet, exercise, and medication can prevent cardiovascular diseases.
Diabetes Screening
Diabetes is a prevalent condition among seniors, with many individuals unaware they have it. Screening for diabetes typically involves a fasting blood sugar test or an HbA1c test, which measures average blood sugar levels over the past three months. Early detection and management of diabetes can prevent severe complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and vision problems.
Bone Density Test
Osteoporosis, characterized by weak and brittle bones, is common in older adults, especially women. A bone density test, or DEXA scan, measures bone mineral density and helps assess the risk of fractures. Early detection of osteoporosis allows for interventions like medication, dietary changes, and exercise to strengthen bones and reduce fracture risk.
Cancer Screenings
Cancer risk increases with age, making regular cancer screenings crucial for seniors. Common screenings include:
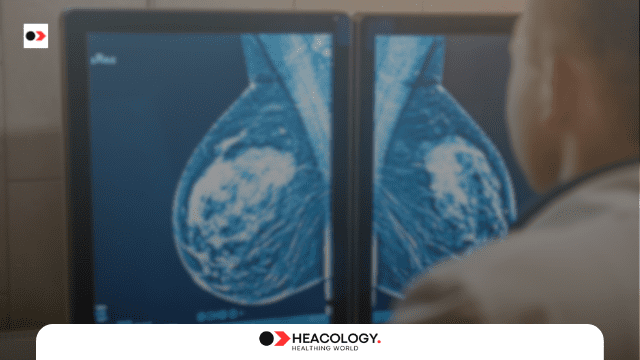
- Mammograms for breast cancer
- Pap smears and HPV tests for cervical cancer
- Colonoscopy for colorectal cancer
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test for prostate cancer
These screenings can detect cancer at an early stage when it is most treatable, significantly improving survival rates.
Vision and Hearing Tests
As we age, our vision and hearing often decline. Regular vision and hearing tests can detect problems early, allowing for corrective measures like glasses, hearing aids, or treatments for conditions such as cataracts and glaucoma.
Mental Health Screenings
Mental health is just as important as physical health, particularly in older adults who may experience issues such as depression, anxiety, or cognitive decline. Regular mental health screenings can help identify these conditions early, enabling timely intervention and support.
The Role of Primary Care in Health Screenings
Continuity of Care
Primary care providers play a crucial role in the regular health screenings of seniors. They offer continuity of care, meaning they are familiar with the patient's health history and can provide personalized screening recommendations. This personalized approach ensures that seniors receive the most appropriate screenings for their specific health needs.
Coordinated Care
Primary care providers also coordinate care with specialists, ensuring that any health issues detected during screenings are managed effectively. This coordinated care approach helps prevent gaps in treatment and ensures comprehensive care for seniors.
Health Education and Counseling
Primary care providers educate seniors about the importance of health screenings and guide them on maintaining a healthy lifestyle. This education is vital for encouraging seniors to participate in regular screenings and adhere to preventive measures.
Recommended Frequency of Health Screenings for Seniors
The frequency of health screenings for seniors depends on various factors, including age, sex, family history, and existing health conditions. Here are general guidelines for some common screenings:
- Blood Pressure Checks: At least once a year
- Cholesterol Levels: Every 4-6 years, more often if at risk for heart disease
- Diabetes Screening: Every 3 years, more frequently if overweight or at risk
- Bone Density Test: Every 2 years for women over 65 and men over 70, or younger if at risk
- Cancer Screenings: Varies by type; discuss with healthcare provider
- Vision and Hearing Tests: Every 1-2 years
- Mental Health Screenings: Annually, or more frequently if experiencing symptoms
Overcoming Barriers to Regular Health Screenings
Accessibility and Affordability
One of the significant barriers to regular health screenings is accessibility and affordability. Many seniors may find it challenging to access healthcare services due to physical limitations or financial constraints. Addressing these barriers through community health programs, mobile clinics, and affordable healthcare plans can help ensure that all seniors have access to essential screenings.
Awareness and Education
Lack of awareness about the importance of regular health screenings can also prevent seniors from seeking these services. Healthcare providers and community organizations should focus on educating seniors and their caregivers about the benefits of screenings and the risks of neglecting them.
Support Systems
Having a strong support system can encourage seniors to participate in regular health screenings. Family members, friends, and caregivers play a crucial role in reminding and assisting seniors with scheduling and attending their screenings.
FAQs
Why Are Health Screening Tests Important?
Health screening tests are essential because they help identify potential health issues before symptoms appear. Early detection is critical for successful treatment and management of many conditions. For seniors, this can mean catching diseases like diabetes, hypertension, and cancer at a stage where they can be more effectively treated. Regular screenings can also monitor existing health conditions, ensuring that they are managed properly and do not worsen over time. Overall, health screenings play a vital role in maintaining optimal health and preventing serious complications.
Why Is Screening Important in Primary Care?
Screening is a crucial aspect of primary care because it allows healthcare providers to proactively manage a patient's health. By regularly conducting screenings, primary care providers can detect diseases early, often before the patient has any noticeable symptoms. This early intervention can significantly improve health outcomes. Additionally, primary care providers can offer personalized screening recommendations based on an individual's health history, risk factors, and lifestyle. This personalized approach ensures that patients receive the most relevant and necessary screenings for their specific health needs, promoting better overall health management.
Which Screening Modality Is Pertinent to the Older Adult Population?
Several screening modalities are particularly pertinent to the older adult population. Some of the most important include:
- Blood Pressure Checks: Essential for detecting hypertension, a common condition in seniors.
- Cholesterol Levels: Important for assessing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Diabetes Screening: Critical for early detection and management of diabetes.
- Bone Density Test: Helps diagnose osteoporosis and assess fracture risk.
- Cancer Screenings: Including mammograms, Pap smears, colonoscopies, and PSA tests, which are vital for early cancer detection.
- Vision and Hearing Tests: Necessary for identifying age-related decline in these senses.
- Mental Health Screenings: Important for detecting issues like depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline.
These screenings help in maintaining the overall health and well-being of seniors by identifying and addressing potential health issues early.
How Often Should You Do a Health Screening?
The frequency of health screenings can vary based on age, health status, and risk factors, but general guidelines for seniors include:
- Blood Pressure Checks: At least once a year.
- Cholesterol Levels: Every 4-6 years, more often if there is a high risk of heart disease.
- Diabetes Screening: Every 3 years, more frequently if overweight or at high risk.
- Bone Density Test: Every 2 years for women over 65 and men over 70, or younger if at risk.
- Cancer Screenings: Frequency varies by type; consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
- Vision and Hearing Tests: Every 1-2 years.
- Mental Health Screenings: Annually, or more frequently if experiencing symptoms.
Following these guidelines can help seniors maintain their health and catch potential issues early, leading to better health outcomes and improved quality of life.
Conclusion
Regular health screenings are a cornerstone of preventive healthcare for seniors. They play a vital role in early disease detection, monitoring chronic conditions, and promoting overall health and well-being. By understanding the importance of these screenings and following the recommended guidelines, seniors can take proactive steps towards maintaining their health and enjoying a higher quality of life. Healthcare providers, caregivers, and community organizations must work together to ensure that seniors have access to the necessary screenings and the support they need to stay healthy.











Your Opinion Is Important For Us!